(and how it could save your life)
You may have heard me say it before – “it is so important to lower your omega 6: omega 3 ratio…..” But why? What is the difference between these two types of fatty acids? Should you really be concerned??
The answer – absolutely YES! Biochemically speaking (and put on your thinking caps for this one), omega-3 and omega-6 are both polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs); the main difference between the two is that the last double bond is 6 carbons away from the omega end of the fatty acid molecule in omega-6, while only 3 carbs away in omega-3. This might not mean much to you; in fact, you may be thinking they both sound pretty similar. However, the difference could not be more drastic or pronounced in terms of the harm an unbalanced ratio can have on your body.
Lets break it down:
- Humans essentially evolved on a 1:1 ratio of omega-6: omega-3 fatty acids
- Our genetic patterns and overall development thrived on this very particular ratio.
- Fast forward to modern day… the ratio of omega-6: omega-3 fatty acids in the Western Diet, on average, is an astounding 15:1. Yes, FIFTEEN TO ONE.
- When Omega 6 is broken down during normal body processes, the by-products are HIGHLY inflammatory?
- The more Omega 6, the more inflammation, and the diseases associated with it
It is no wonder the prevalence of disease, specifically cardiovascular disease, cancer, and inflammatory-driven, autoimmune diseases, in Western societies is continuously sky-rocketing. It will get worse unless we make radical changes to our omega-6: omega-3 fatty acid consumption. Omega-3s have been shown to have profound anti-inflammatory effects; in fact, increased dietary intake of these fatty acids can positively alter the manifestation of disease. Amazing results published in a recent abstract, show promising benefits of lowering this ratio:
- 4:1 omega-6: omega-3 ratio was associated with a 70% decrease in total mortality
- decreased omega-6: omega-3 ratio exerted suppressive effects on cardiovascular disease, cancer, and inflammatory-driven, autoimmune diseases
- 2.5:1 omega-6: omega-3 ratio successfully reduced inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- 10:1 omega-6: omega-3 ratio had adverse health consequences
I sincerely hope the importance and significance of a low omega-6: omega-3 ratio in your diet is clear.
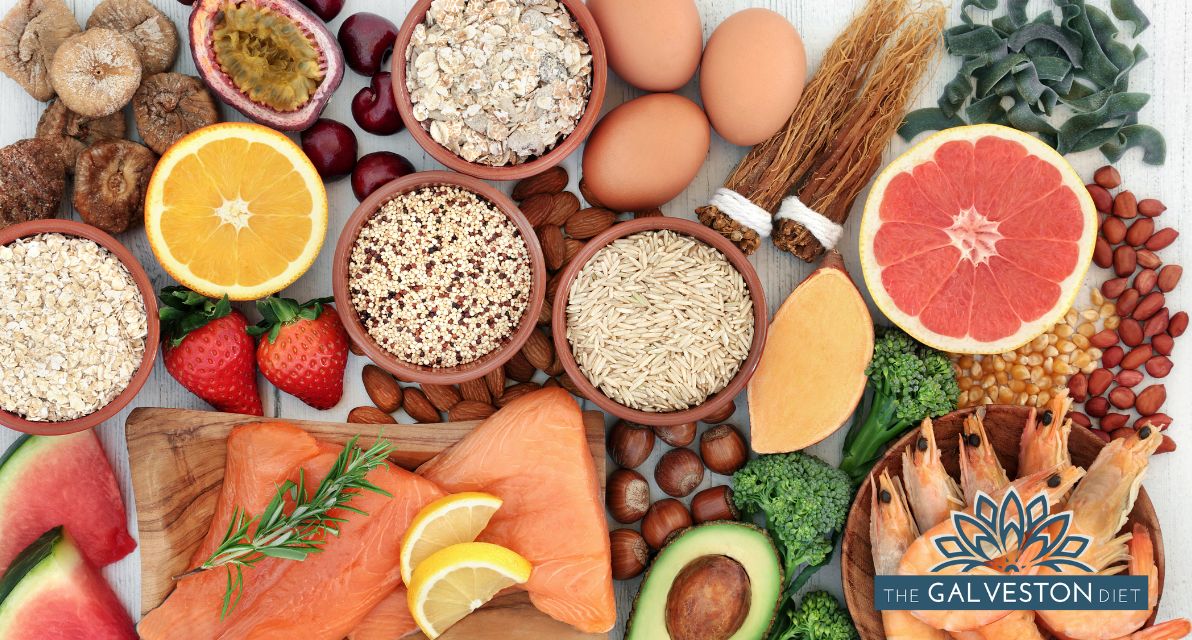
In the Galveston Diet Signature Program, we explore this concept in more detail and I provide tips and tricks to ensure this ratio is as close to 1 as possible. In short, increase consumption of high omega-3 fatty acids– my favorite foods to do so are below:
- Avocado
- Fatty Fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
- Flaxseeds
- Chia Seeds
- Walnuts
- Eggs
- Leafy Greens (brussel sprouts, kale, spinach, broccoli, cauliflower)
Article References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0753332206002435
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12442909
https://www.webmd.com/diet/guide/your-omega-3-family-shopping-list#1
If you are interested in learning more about the science behind The Galveston Diet, Click Here.